In the battle against climate change, both Direct Air Capture (DAC) and plant-based carbon sequestration offer promising solutions. While DAC employs cutting-edge technology to remove carbon dioxide (CO2) directly from the atmosphere, plant-based sequestration harnesses the natural ability of plants to capture and store CO2. Here, we will explore both methods, emphasizing the unique benefits of plant-based sequestration and the innovative use of biochar.

Understanding Direct Air Capture (DAC)
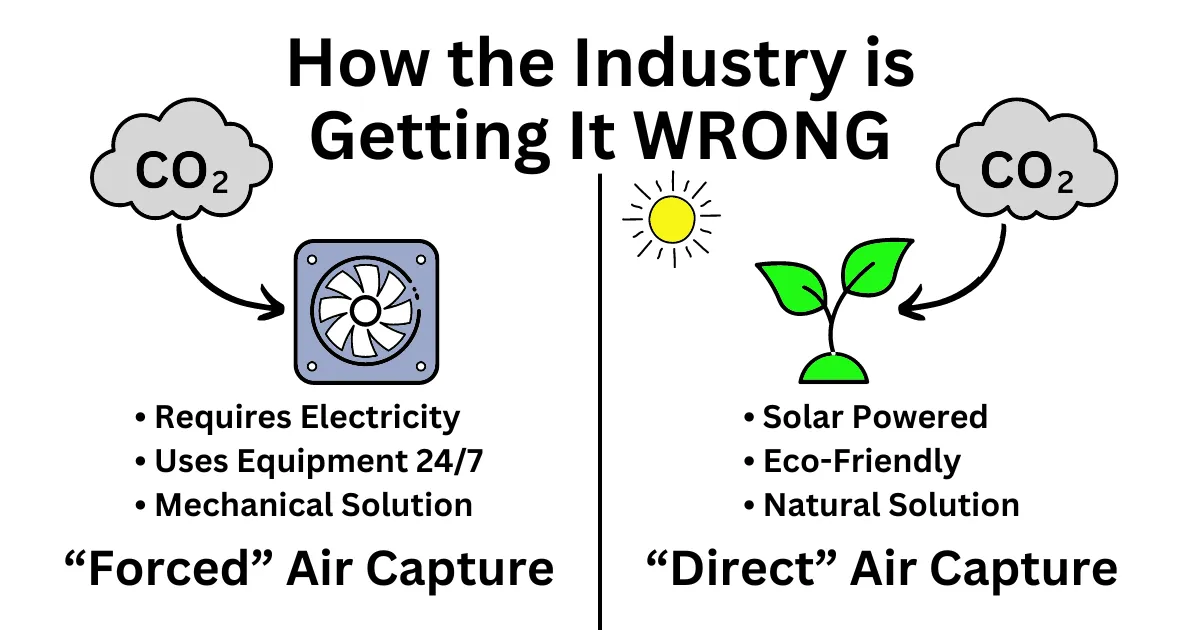
Direct Air Capture is a technology-driven approach to carbon sequestration. The process involves using chemical reactions to capture CO2 directly from the air. Here’s how it works:
- Air Intake: Large fans draw ambient air into the DAC system.
- CO2 Capture: The air passes through a chemical solution or solid sorbent that selectively binds with CO2 molecules.
- CO2 Release: The CO2-saturated sorbent or solution is treated to release the captured CO2.
- CO2 Storage or Utilization: The pure CO2 is compressed and either stored underground or utilized in various industrial processes.
Benefits of DAC
- Scalability: Capable of being scaled up to capture large amounts of CO2.
- Location Flexibility: Can be deployed anywhere, not limited by the location of emissions.
- Negative Emissions: Removes existing CO2 from the atmosphere, contributing to negative emissions.
Challenges of DAC
- High Costs: Currently more expensive than other sequestration methods.
- Energy Intensive: Requires significant energy input, which can be mitigated with renewable energy sources.
- Technological Dependence: Relies on advanced technology and infrastructure.
Understanding Plant-Based Carbon Sequestration
Plants naturally capture CO2 from the air through the process of biosynthesis. This captured carbon is stored in plant biomass and soil. Dynamic Carbon Credits focuses on enhancing this natural process by utilizing biochar, a stable form of carbon produced from plant matter.
- Biosynthesis: Plants absorb CO2 from the atmosphere and convert it into organic matter.
- Carbon Storage in Biomass: Carbon is stored in the plant’s roots, stems, and leaves.
- Biochar Production: Plant biomass is converted into biochar through pyrolysis, a process that involves heating organic material in the absence of oxygen.
- Soil Amendment: Biochar is added to the soil, where it can store carbon for centuries while improving soil health.
Benefits of Plant-Based Sequestration with Biochar
- Cost-Effective: Generally less expensive than DAC, making it more accessible for widespread adoption.
- Soil Health Improvement: Biochar enhances soil fertility, water retention, and microbial activity, leading to better plant growth and increased agricultural productivity.
- Long-Term Carbon Storage: Biochar is highly stable, ensuring that captured carbon remains sequestered for hundreds to thousands of years.
- Sustainability: Uses natural processes and renewable resources, reducing reliance on technological infrastructure.
- Co-Benefits: Supports biodiversity, reduces soil erosion, and can help restore degraded lands.
Comparative Analysis
While both DAC and plant-based sequestration with biochar have their merits, plant-based solutions offer several unique advantages:
- Economic Viability: Plant-based sequestration, particularly with the use of biochar, is generally more cost-effective than DAC. This makes it a more feasible option for widespread implementation, especially in developing regions.
- Soil and Ecosystem Benefits: Unlike DAC, which is primarily focused on CO2 removal, plant-based sequestration with biochar provides significant co-benefits for soil health, agricultural productivity, and ecosystem restoration.
- Simplicity and Accessibility: Plant-based methods leverage natural processes that are easily understood and implemented, even in low-tech settings. This accessibility can drive broader participation in carbon sequestration efforts.
Conclusion
In the pursuit of sustainable carbon sequestration solutions, both Direct Air Capture and plant-based methods have important roles to play. However, plant-based sequestration, especially when enhanced with biochar, offers a cost-effective, sustainable, and multi-beneficial approach. By investing in and promoting plant-based sequestration, we can not only capture and store carbon but also improve soil health, support biodiversity, and boost agricultural productivity.
For corporate executives, sustainability professionals, and eco-conscious individuals, embracing plant-based sequestration with biochar presents a compelling opportunity to achieve carbon neutrality and foster a healthier planet. To learn more about innovative carbon sequestration solutions and explore investment opportunities in carbon credits, visit Dynamic Carbon Credits and join us in our mission to combat climate change and promote sustainability.